 |
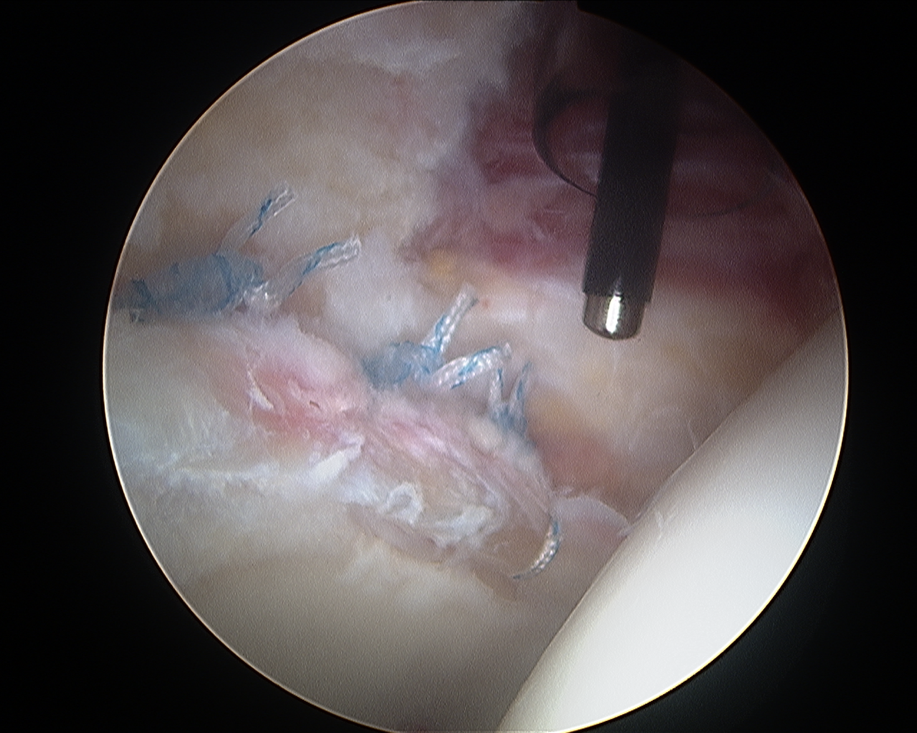 |
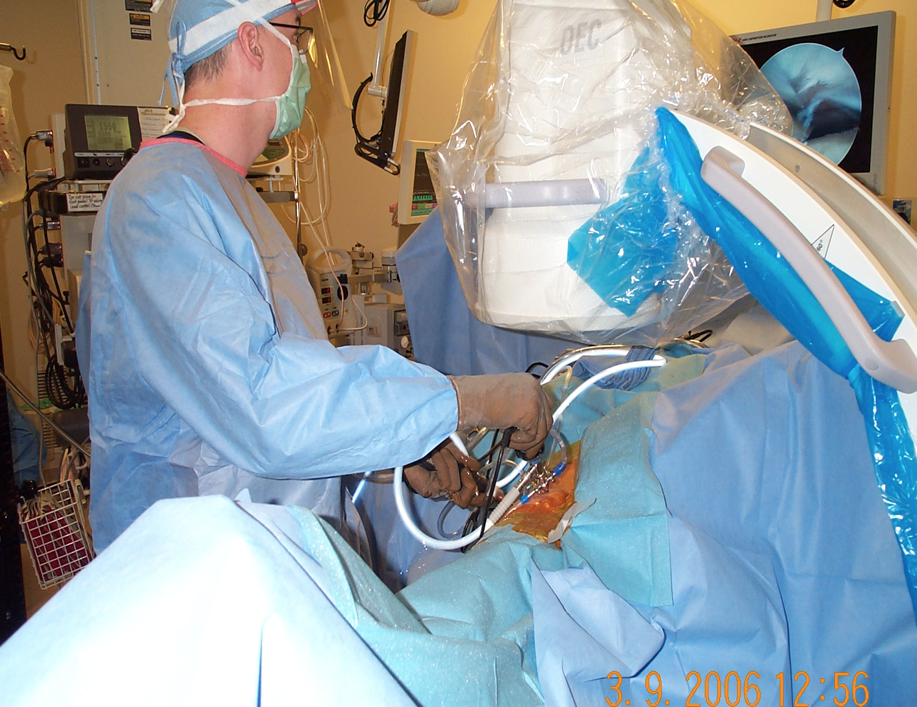
| Dr. Stewart performing hip arthroscopy | Image of a labral tear repaired arthroscopically |
One of the more common hip conditions that hip arthroscopy is used to treat is femoracetabular impingement (FAI). Femoracetabular impingement is a deformity that develops at the hip joint from abnormal pressure and friction between the ball and socket of the hip joint which results in pain and hip dysfunction. There are two types of femoracetabular impingement, CAM type and pincer type. CAM type of impingement is when there is excess bone growth on the head of the femur. Pincer type of impingement is when there is excess bone growth along the rim of the acetabulum. Femoracetabular impingement is the most common cause of a labral tear, which is the cartilage that is located at the edge of the acetabulum. Untreated femoracetabular impingement can lead to an early development of osteoarthritis and the need for hip replacement.
 |
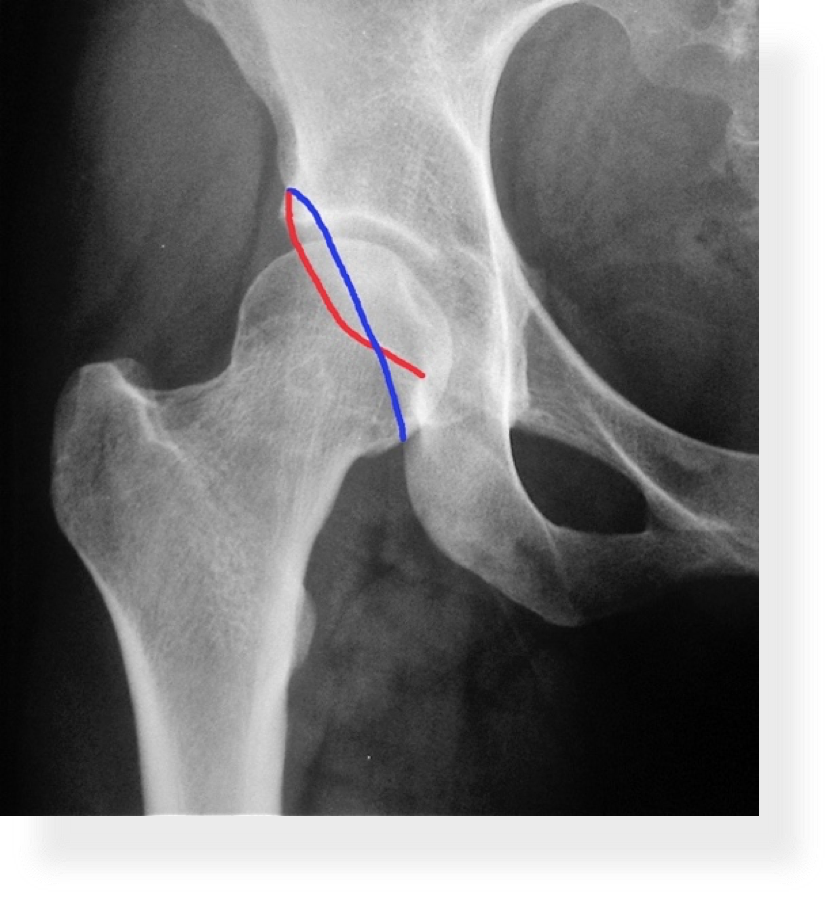 |
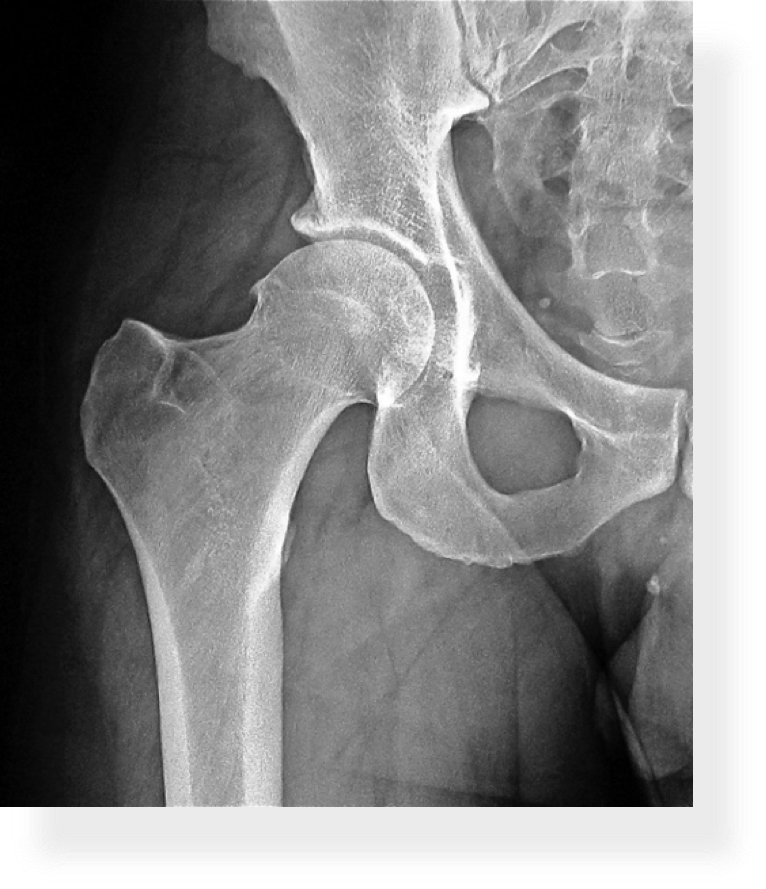
| CAM Type Impingement | Pincer Type Impingement |
Hip arthroscopy is an outpatient surgical procedure and therefore, patients go home the same day as their surgery. The hip arthroscopy procedure generally takes 1-2 hours. Patients will typically need assistance for the first 1-2 days postoperatively. Our patients begin outpatient physical therapy the day after their surgery. Supervised physical therapy is continued for up to 12 weeks postoperatively. All of our patients take naproxen twice daily for 21 days after surgery to reduce the risk of excess bone growth at the surgical site, called heterotopic ossification. Our patients are also put on aspirin postoperatively to reduce the risk of developing a blood clot. Generally, our patients use crutches for the first 2-3 weeks postoperatively. After hip arthroscopy, patients are able to return to light duty work 2-4 weeks after surgery. In general, patients can return to heavy duty work 4-6 weeks after surgery. However, every patient recovers at a different pace and therefore, return to work status is addressed at the 2 week postoperative follow up appointment.



